Strong infrared laser pulses can extract an electron from a molecule (ionization), accelerate it away into free space, then turn it around (propagation), and finally collide it with the molecule (recollision). This is the widely used three-step model of strong-field physics. In the recollision step, the electron may, for example, recombine with the parent ion, giving rise to high harmonic generation, or scatter elastically, giving rise to laser-induced electron diffraction.
Laser-driven electron recollision remembers molecular orbital structure
One of the commonly used assumptions underlying attosecond physics is that, in the propagation step, the initial structure of the ionized electron is "washed out", thus losing the information on the originating orbital. So far, this assumption was not experimentally verified in molecular systems.
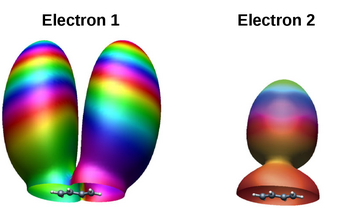
A combined experimental and theoretical study at the Max Born Institute Berlin investigated the strong-field driven electron recollision dynamics in the 1,3-trans-butadiene molecule. In this molecule, the interaction with the strong laser field leads mainly to the ionization of two outermost electrons exhibiting quite different densities, see Figure 1. The state-of-the-art experiments and simulations then allowed the scientists to measure and calculate the high-angle rescattering probability for each electron separately. These probabilities turned out to be quite different both in the measurements and in the simulations. These observations clearly demonstrate that the returning electrons do retain structural information on their initial molecular orbital.