In photochemistry and molecular photovoltaics, so-called transition metal complexes are a widely used system. It consists of a central metal ion bound to a group of mostly organic ligands. These materials show strong absorption of visible or ultraviolet light - an attractive property for applications as primary light absorbers in molecular solar cells or in molecular optoelectronics. After absorption of light, an extremely fast transfer of the electrons from the metal ion to the ligands is observed. This mechanism is essential to generate an electrical voltage. Since solid state materials are preferred in all applications, the transition metal complexes are packed very densely in these, which leads to a strong interaction with one another. So far no information was available on the influence of this mutual interaction on the ultrafast electron motion after light absorption.
Synchronous motion of electrons in neighboring molecules - an ultrafast X-ray film over metal complexes in a crystal
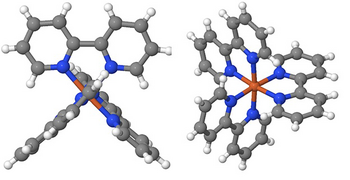
Fig. 1 Ball and rod model of the transition metal complex iron (II) tris-bipyridine [Fe(bpy)3]2+. Iron atoms (Fe) are brown, nitrogen (N) blue, carbon (C) gray and hydrogen (H) white spheres. The six nitrogen atoms are located at the corners of an octahedron centered around the Fe atom. The levels of the 3 bipyridine subunits (N2C10H8) are perpendicular to each other.
In order to follow such an ultrafast electron motion directly in space and time, one needs experimental methods that measure the position of electrons in a crystal with a precision of (0.1 nm = 10-10m), such as the distance between neighboring atoms, on a sub-atom. 100 fs time scale (1 fs = 10-15s). Such an imaging is possible when ultrashort X-ray flashes are scattered at the electrons, since the diffraction pattern provides the information about the spatial arrangement of the electrons. The motion of the electrons is triggered by a short, optical pulse of light, which excites a single electron on an individual metal complex. Benjamin Freyer, Flavio Zamponi, Vincent Juve, Johannes Stingl, Michael Wörner, Thomas Elsässer and Majed Chergui report on the first in-situ X-ray imaging of the Journal of Chemical Physics 138, 144504 (2013) (free download) Electron and atomic motions triggered by such an electron transfer reaction. For the prototype material, they show [Fe(bpy)3]2+ (PF6-)2, time-dependent "electron density maps," obtained from individual snapshots using 100 fs short X-ray flashes. A series of snapshots for different moments, i. before, during, and after the electron transfer reaction can be combined into an ultrafast X-ray film via electron and atom motions.
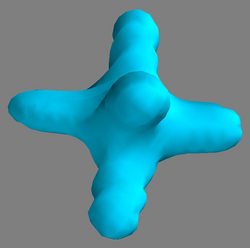
Fig. 2 The counterions in our crystal are each two hexa-fluoro-phosphate (PF6) ions [phosphorus (P), fluorine (F)]. The six F atoms are also located at the corners of an octahedron around the central P atom. Here we show a 3-dimensional surface of constant electron density ρ(r, t) = ρC = const. The value for ρC was chosen so that one can trace the movement of the electrons on the (PF6-) anion most sensitively. In the accompanying X-ray film, a significant outflow (i.e., shrinkage of the isoelectronic density surface) of electrons from the (PF6-) anion after light-excitation is observed.
To the great surprise of the scientists, the time-dependent "electron density maps" showed not only a shift of electrons from the iron atoms to the bipyridine ligands, but also - a previously unexpected - shift of electrons from the PF6- anions to the bipyridine ligands. A detailed analysis of the X-ray snapshots shows that the electron transfer occurs on about 30 metal complexes (each with 2 PF6- anions) around the directly light-excited complex. This collective response of the electrons is caused by the strong Coulomb forces between the different ions, which strive to minimize the total electro-static energy of the crystal. Such behavior is most welcome for the collection of electrical charge in opto-electronic devices.
Search publications of MBI
Publications since 2025