Search results 311
until 320
of 5664
Dr. Federico Furch named 2018 OSA Ambassador
 In October of 2017 the Optical Society (OSA) announced the 2018 class of OSA Ambassadors. One member of this class is MBI researcher Dr. Federico Furch, who in the last few years has been responsible…
In October of 2017 the Optical Society (OSA) announced the 2018 class of OSA Ambassadors. One member of this class is MBI researcher Dr. Federico Furch, who in the last few years has been responsible…
From insulator to conductor in a flash
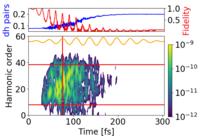 A clever combination of novel technologies enables us to study promising materials for the electronics of tomorrow. Over the past decades, computers have become faster and faster and hard disks and…
A clever combination of novel technologies enables us to study promising materials for the electronics of tomorrow. Over the past decades, computers have become faster and faster and hard disks and…
Freeing electrons to better trap them
 For the first time, researchers from UNIGE and MBI in Berlin have placed an electron in a dual state - neither freed nor bound - thus confirming a hypothesis from the 1970s. Atoms are composed of…
For the first time, researchers from UNIGE and MBI in Berlin have placed an electron in a dual state - neither freed nor bound - thus confirming a hypothesis from the 1970s. Atoms are composed of…