Researchers at the Max Born Institute in Berlin observed the extremely rapid development of electrical resistance in a semiconductor by tracking the movement of electrons in real time.
How fast is the electrical resistance?
When you first heard of electric current, you may have wondered how the electrons in a solid move from negative to positive. In principle, it is possible for the electrons to "fly" through the solid without being affected by the atoms or other charges in the material. Under normal conditions, this does not happen because the electrons collide with the vibrating nuclei or with impurities. Typically, such shocks happen after an extremely short time, about 100 femtoseconds (10-13 seconds, one tenth of a trillionth of a second). Thus, the movement of electrons in the material is like a movement through a dense crowd, not like a run along an empty street. Therefore, a typical electron velocity is only 1 m / h (not km / h!), Slower than a snail.
Although the electrons abut very often in the material, such impacts take a finite time. When you push yourself through a crowd, there are sometimes small empty areas where you can go faster. If you observe the electrons moving on a very fast (femtosecond) time scale, you would expect the electrons to fly undisturbed through the material for a very short time after turning on the battery before they hit anything. That's exactly what researchers at the Max Born Institute in Berlin recently did, and what they're reporting on in the latest issue of Physical Review Letters [Volume 107, 256602 (2011)]. Extremely short pulses of terahertz of light (1 terahertz = 1012 Hz, 1 trillion oscillations per second) were used instead of a battery (light has an electric field like a battery) to accelerate optically generated free electrons in a piece of gallium arsenide. The accelerated electrons in turn generate another electric field. If you measure this field with femtosecond time resolution, you can see exactly what the electrons are doing. The researchers saw that the electrons were accelerated undisturbed immediately after switching on the electric field, whereas the impact was only noticeable after about 300 femtoseconds.
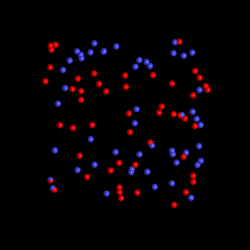
In the attached movie we show what happens in the gallium arsenide crystal. Electrons (blue balls) and holes (red balls) show random heat movements before the terahertz pulse hits the sample. The electric field (green arrow) accelerates electrons and holes in opposite directions. In the emergence of electrical resistance, this movement is slowed down. This leads to a heated electron-hole gas, that is, to a faster thermal movement.
These experiments allowed the researchers to determine which type of impact is mainly responsible for electrical resistance. Interestingly, they found out that the most important colliding partners are not atomic vibrations, but positively charged particles called holes. A hole or hole is an empty electron state in the valence band of the semiconductor; it has a positive charge and about 6 times the mass of the electron. The optical excitation of a semiconductor simultaneously generates free electrons and holes. These are moved in opposite directions by the terahertz pulse, our battery. Since the holes have a much larger mass compared to the electrons, they move only slowly, but they are in the way of the electrons, which slows them down.
The understanding of the processes leading to the deceleration of electrons can lead to more efficient and faster electronics in the future and perhaps to new tricks to reduce the electrical resistance.
Search publications of MBI
Publications since 2025