The semiconductor electronics are based on the generation, control and amplification of electrical currents in components such as the transistor. Carriers of the electric current are free-moving electrons, which travel at high speed through the crystal lattice of the semiconductor. In doing so, they lose part of their kinetic energy by causing the atoms of the crystal lattice to vibrate. In semiconductors such as gallium arsenide, the positively and negatively charged ions of the crystal lattice are deflected and oscillate with an extremely short period of 100 fs (1 fs = 10-15 s = 1 billionth of a millionth of a second). In the microcosm of electrons and ions, the vibrational motion is quantized. This means that the energy of this oscillation can only be an integer multiple of a vibrational quantum, a so-called phonon. In the interaction of an electron with the crystal lattice, the so-called electron-phonon interaction, energy packets are transmitted in the form of individual vibrational quanta.
Electrons and lattice vibrations - a strong team in the nanocosmos
As Berlin researchers report in the latest issue of the journal Physical Review Letters, the strength of the electron-phonon interaction is sensitive to the size of the electron, i. from the spatial extent of its charge cloud. Experiments in the time domain of the phonon oscillation period show that for a reduced extension of the electron cloud an up to 50-fold enhanced interaction occurs. As a result, the movements of the electrons and the ions can be so strongly coupled to each other that the individual movements are no longer recognizable. Electron and phonon form a new quasiparticle, a polaron.
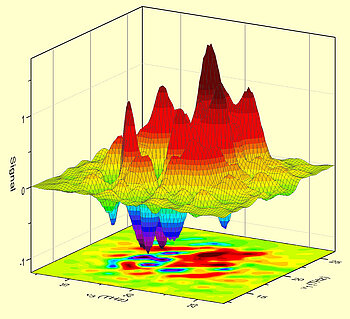
To visualize this phenomenon, scientists used nanostructures of gallium arsenide and gallium aluminum arsenide in which the energies of the electrons and ion motion were matched. The coupling of the movements was made visible with a new optical process. The system is excited by several ultrashort pulses of light in the infrared and the light field emitted by the moving charges is measured in real time. The measurements yield so-called two-dimensional non-linear spectra (see Fig.), In which coupled optical transitions appear separated and from which the coupling strength between electrons and phonons can be derived. The evaluation of the measured data results in the extension of the electron charge cloud, which is only 3-4 nanometers (1 nanometer = 10-9 m = 1 billionth of a meter). In addition, the new method demonstrates for the first time the strong influence of the electron-phonon coupling on the optical spectra of the semiconductor. This offers interesting perspectives for the development of optoelectronic devices with tailored optical and electrical properties.
Search publications of MBI
Publications since 2025