3.1 Dynamics of Condensed Phase Molecular Systems
Project coordinators: E. T. J. Nibbering , O. KornilovPhase 6 (2018-2024): Ultrafast dynamics and interactions of interfacial water around phosphate groups and around hydrated protons
The people involved:
Jakob Schauss, Achintya Kundu, Fabian Dahms, Jia Zhang, Erik T. J. Nibbering, Benjamin Fingerhut, Thomas Elsaesser
National and international collaboration: Ehud Pines,† Shavkat I. Mamatkulov,o Florian N. Brünig,* Roland Netz.* Douwe Jan Bonthuis,+
†: Department of Chemistry, Ben Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, 84105 Israel.
o: Institute of Material Sciences of Uzbekistan Academy of Sciences, Tashkent100084, Uzbekistan.
*: Fachbereich Physik, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin14195, Germany.
+: Institute of Theoretical and Computational Physics, Graz University of Technology, Graz8010, Austria.
Phase 6 (2018-2024):
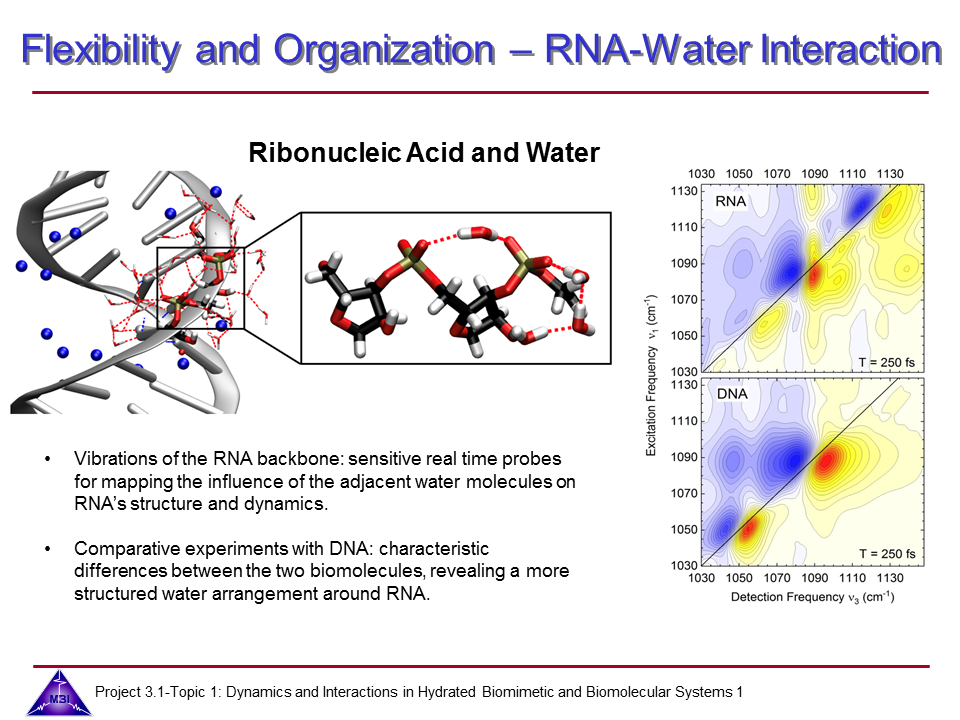
In the sixth period we aim to tackle with in-depth detail the dynamics and interactions of interfacial water around phosphate groups, as hydrated ions in solution or as key structural units in the sugar-phosphate backbones of DNA and RNA. We further explore the ultrafast dynamics of hydrated protons subject to various solution conditions.
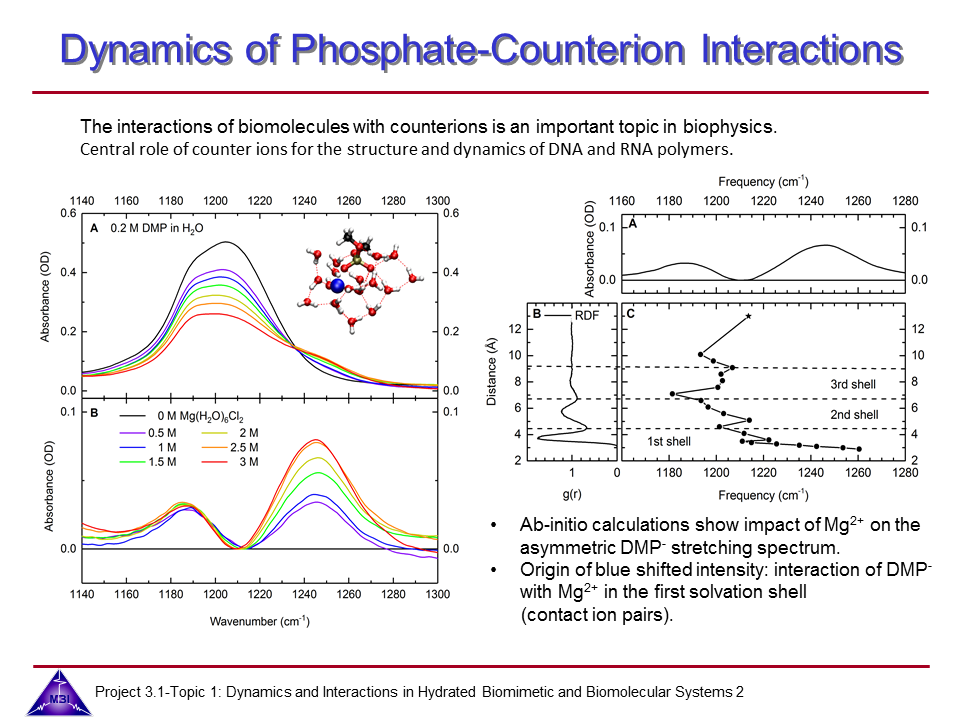
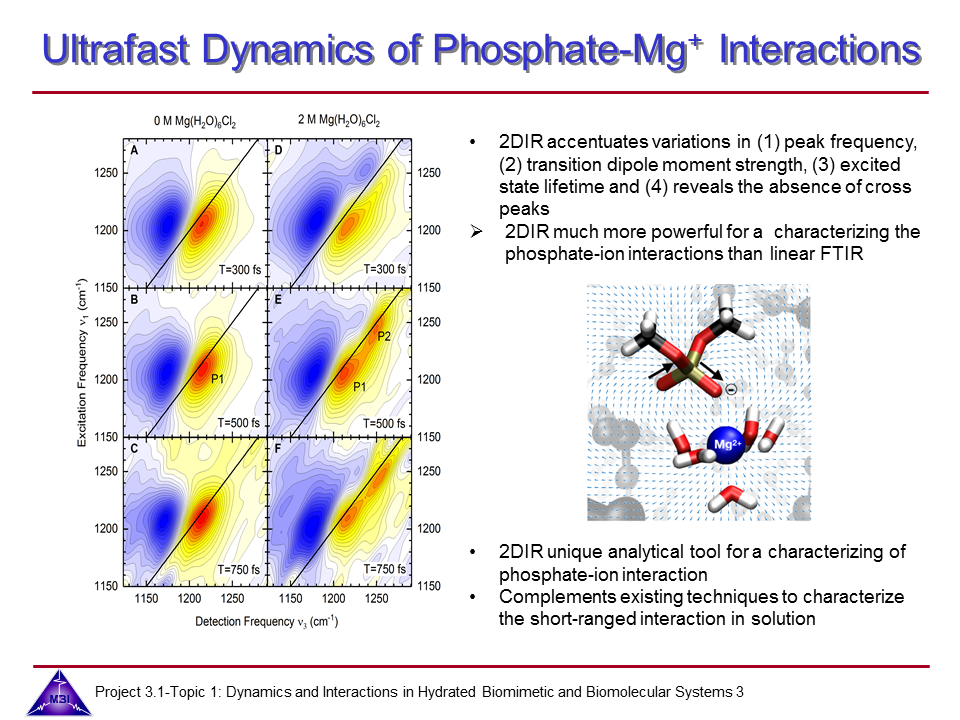
6-1 Ultrafast dynamics of hydrated phosphate-counterion interactions
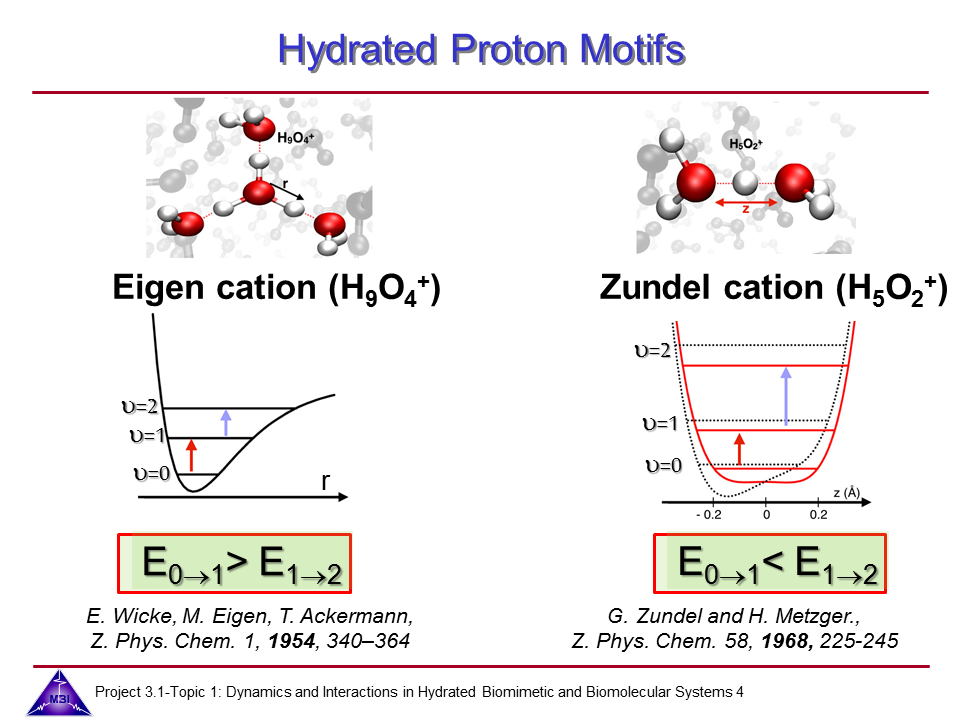
6-2 Ultrafast dynamics of hydrated excess protons